Basics
A. Indexing/Barcoding
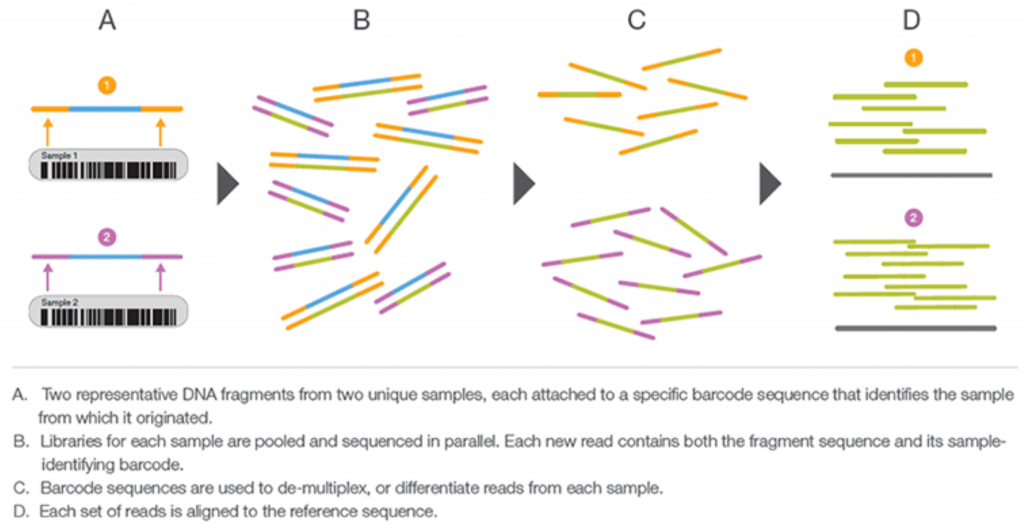
As shown in the figure below, indexing, also called barcoding, is appending short nucleotide “barcode” to each library using specific adapters containing the barcode (A). Libraries are constructed to contain different indexed adapters, quantified, and pooled in equimolar amounts (B). After sequencing, the sequence reads are deconvoluted informatically to each library on basis of these barcodes (C). Indexing allows for the sequencing of multiple libraries in a single mixture, i.e., multiplexing, at a potential cost and time saving. Assigning barcodes correctly to the right samples is critical in multiplexing and de-multiplexing.
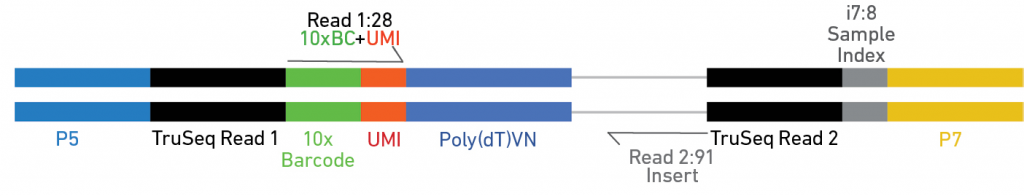
Unique Molecular Index (UMI) is a sequence barcode appended to each DNA molecule during library preparation. UMI is usually used, in addition to library indices, to distinguish independent DNA molecules from PCR duplicates. Generally, UMI (12 – 16 bp) are longer than library indices (6 – 10 bp), located just after Index 1. The following figure is a schematic representation of UMI application in 10× Genomics Chromium single-cell gene expression analysis, in which UMI is located just after 10× barcode in Read 1.
B. Illumina Sequencing-by-Synthesis (SBS) Technology
To explore Illumina massively parallel sequencing with optimized SBS chemistry, please refer to the Illumina sequencing introduction as well as the Illumina website.

The figure above is a schematic representation of a dual-indexed library fragment for Illumina paired-end sequencing. Arrows indicate four sequencing primers (SP) used for the four sequencing reactions in order: Read 1 (Rd1), Index 1 (In1), Index 2 (In2), and Read 2 (Rd2). The library is a pool of molecules that look like this, all containing a DNA fragment of interest as the insert (100 – 600 bp) with adapters on either end having the composition indicated above.
C. PacBio Single-Molecule Real-Time (SMRT) Sequencing Technology
To learn how PacBio SMRT sequencing works, please refer to PacBio Website.
As shown in the figure, PacBio uses a SMRTbell library format, in which DNA fragments are capped on both ends with ligated hairpin adapters, where the sequencing primers attach. This creates a circular template for the polymerase to navigate. 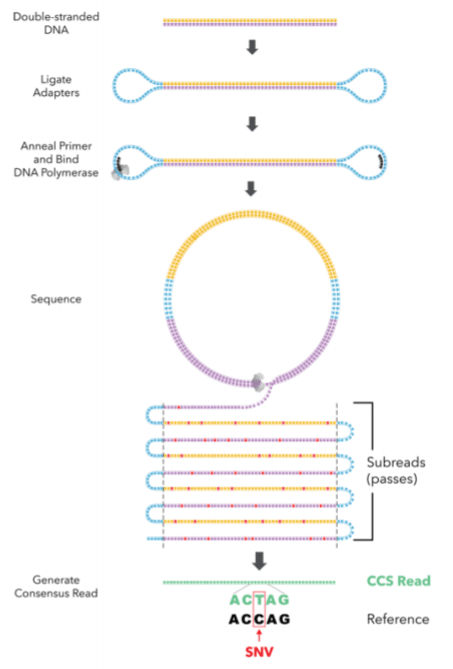
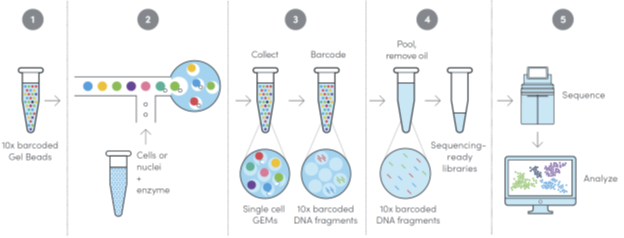
D. 10x Genomics Next GEM Technology
The 10× Genomics Chromium Controller uses advanced microfluidics to perform single cell partitioning and barcoding in a matter of minutes. For more detail, please refer to the figures below and 10× Genomics website.